Exploring The Fascinating Food Web Of The Desert
Deserts might seem like barren wastelands, but beneath the sand dunes lies a complex food web of the desert that's teeming with life. It's like a hidden world where every creature plays a vital role in maintaining balance. This ecosystem operates in a way that's both brutal and beautiful, and understanding it can teach us a lot about survival and adaptation.
When you think about deserts, the first image that pops into your mind might be endless sand and scorching heat. But there's so much more to it than meets the eye. The food web of the desert is an intricate network of relationships between plants, animals, and microorganisms. It's like a big puzzle where every piece matters. If one piece goes missing, the whole system can collapse.
This article dives deep into the fascinating world of desert ecosystems. We'll explore the key players, their roles, and how they interact with one another. By the end, you'll have a clearer picture of how life thrives in one of the harshest environments on Earth. So, buckle up and get ready to learn something incredible!
- Abigail Shapiro Controversy Unveiling The Truth Behind The Headlines
- Jersey City Shopping Mall Your Ultimate Urban Retail Destination
Table of Contents
- Introduction to the Food Web of the Desert
- Primary Producers: The Desert's Green Powerhouses
- Herbivores: Nature's Grazers in the Desert
- Carnivores: The Desert's Apex Predators
- Decomposers: The Unsung Heroes of the Desert
- Water and Survival: The Desert's Greatest Challenge
- Adaptations: How Desert Creatures Thrive
- Human Impact on the Food Web of the Desert
- Conservation Efforts: Protecting the Desert Ecosystem
- Future Perspectives: What Lies Ahead for Desert Ecosystems?
Introduction to the Food Web of the Desert
Deserts are often misunderstood as lifeless places, but the truth is far from that. The food web of the desert is a complex system where energy flows from one organism to another. It's like a giant game of tag, where every creature is either hunting or being hunted. This delicate balance ensures that life continues even in the harshest conditions.
What Makes Deserts Unique?
Deserts are defined by their low rainfall, extreme temperatures, and limited resources. These factors make it a challenging environment for most living things. Yet, the creatures that call the desert home have evolved incredible adaptations to survive. From cacti that store water to reptiles that can go months without drinking, every organism has its own survival strategy.
One of the coolest things about the food web of the desert is how interconnected everything is. A change in one part of the system can have a ripple effect throughout the entire ecosystem. For example, if a key predator disappears, the population of its prey can explode, throwing the balance out of whack.
- Unveiling The Secrets Of Avox In Hunger Games Everything You Need To Know
- Incredibles Villain The Ultimate Guide To Their Backstories And Powers
Primary Producers: The Desert's Green Powerhouses
In any food web, primary producers are the foundation. In the desert, these are mostly plants like cacti, succulents, and drought-resistant grasses. These plants have evolved to survive with minimal water and intense sunlight. They're like the chefs of the desert, converting sunlight into food through photosynthesis.
Key Desert Plants
- Saguaro Cactus: The iconic cactus of the Sonoran Desert, it can live for over 200 years.
- Creosote Bush: One of the oldest living organisms on Earth, it can survive for thousands of years.
- Joshua Tree: Found in the Mojave Desert, it provides food and shelter for many animals.
These plants not only produce food but also provide shelter and habitat for other organisms. They're like the building blocks of the desert ecosystem.
Herbivores: Nature's Grazers in the Desert
Herbivores are the next level in the food web of the desert. These animals feed on the primary producers, converting plant material into energy. Some common desert herbivores include kangaroo rats, desert tortoises, and jackrabbits.
Adaptations of Desert Herbivores
Desert herbivores have developed unique adaptations to survive in such a harsh environment. For example:
- Kangaroo rats can survive without drinking water, getting all their moisture from the seeds they eat.
- Desert tortoises can store water in their bladders for months, allowing them to survive long dry spells.
- Jackrabbits have large ears that help dissipate heat, keeping them cool in the scorching desert sun.
These adaptations are what allow herbivores to thrive in an environment where water is scarce and temperatures are extreme.
Carnivores: The Desert's Apex Predators
Carnivores sit at the top of the food web of the desert. These animals feed on herbivores and other smaller predators, helping to control their populations. Some of the most iconic desert carnivores include coyotes, rattlesnakes, and falcons.
Roles of Desert Carnivores
Carnivores play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of the desert ecosystem. They:
- Prevent overpopulation of herbivores, which could lead to overgrazing and habitat destruction.
- Help remove sick or weak animals, keeping the population healthy.
- Provide food for scavengers and decomposers when they die.
Without carnivores, the desert ecosystem would quickly fall out of balance. Their presence is essential for the survival of the entire food web.
Decomposers: The Unsung Heroes of the Desert
Decomposers might not be as glamorous as carnivores or herbivores, but they're just as important. These organisms break down dead plants and animals, recycling nutrients back into the soil. In the desert, decomposers include fungi, bacteria, and insects like dung beetles.
Why Decomposers Matter
Decomposers are the cleanup crew of the desert. They:
- Recycle nutrients, making them available for plants to use.
- Break down organic matter, reducing waste and preventing disease.
- Support the growth of new life by enriching the soil.
Without decomposers, the desert would quickly become a wasteland of dead organisms. Their work is vital for the health of the entire ecosystem.
Water and Survival: The Desert's Greatest Challenge
Water is the most precious resource in the desert, and every organism has developed strategies to conserve it. Plants store water in their tissues, animals reduce water loss through their skin, and some creatures can even extract moisture from the air.
How Desert Organisms Conserve Water
Here are some examples of how desert organisms adapt to water scarcity:
- Cacti have thick, waxy skin to prevent water loss and spines to protect against predators.
- Camels can go weeks without drinking water, storing fat in their humps for energy.
- Some insects can extract moisture from the air using specialized structures.
These adaptations are what allow life to persist in such a dry environment. Without them, the desert would truly be a lifeless wasteland.
Adaptations: How Desert Creatures Thrive
Desert creatures have evolved incredible adaptations to survive in one of the harshest environments on Earth. These adaptations include physical, behavioral, and physiological changes that help them cope with extreme temperatures, limited water, and scarce food.
Physical Adaptations
Physical adaptations are changes in an organism's body structure that help it survive. Examples include:
- Thick fur or feathers to insulate against cold desert nights.
- Large ears to dissipate heat and improve hearing.
- Specialized kidneys that can concentrate urine, reducing water loss.
Behavioral Adaptations
Behavioral adaptations are changes in an organism's actions that help it survive. For example:
- Many desert animals are nocturnal, avoiding the heat of the day.
- Some creatures burrow into the sand to stay cool and avoid predators.
- Others migrate to cooler areas during the hottest months.
Physiological Adaptations
Physiological adaptations are changes in an organism's internal processes. These include:
- Slowing down metabolism to conserve energy during food shortages.
- Producing antifreeze proteins to prevent freezing in cold desert nights.
- Storing water and nutrients in specialized tissues.
These adaptations are what make desert creatures so remarkable. They've found ways to thrive in an environment where most would struggle to survive.
Human Impact on the Food Web of the Desert
Human activities have a significant impact on desert ecosystems. From habitat destruction to climate change, our actions can disrupt the delicate balance of the food web of the desert. Some of the biggest threats include:
- Urbanization and agriculture, which destroy natural habitats.
- Pollution, which can harm plants and animals.
- Climate change, which alters temperature and rainfall patterns.
It's crucial that we take steps to minimize our impact on these fragile ecosystems. By doing so, we can help preserve the incredible biodiversity of the desert.
Conservation Efforts: Protecting the Desert Ecosystem
Conservation efforts are underway to protect the food web of the desert and the creatures that depend on it. These efforts include:
- Establishing protected areas where human activities are restricted.
- Restoring damaged habitats through reforestation and soil enrichment.
- Monitoring populations of key species to ensure their survival.
Everyone can play a part in conservation by reducing their environmental footprint, supporting conservation organizations, and spreading awareness about the importance of desert ecosystems.
Future Perspectives: What Lies Ahead for Desert Ecosystems?
The future of desert ecosystems depends on how well we can manage the challenges they face. Climate change, habitat destruction, and pollution are all threats that need to be addressed. However, with proper conservation efforts and sustainable practices, there's hope for the survival of these incredible ecosystems.
As we continue to learn more about the food web of the desert, we can develop better strategies for protecting it. By working together, we can ensure that future generations will be able to experience the beauty and wonder of these unique ecosystems.
Kesimpulan
The food web of the desert is a fascinating and complex system that supports a wide variety of life. From primary producers to apex predators, every organism plays a vital role in maintaining balance. Understanding this ecosystem can teach us valuable lessons about survival, adaptation, and the interconnectedness of all living things.
So, the next time you think about deserts, remember that there's more to them than just sand and heat. They're vibrant ecosystems full of life and wonder. And if you're passionate about nature, consider taking action to protect these incredible environments. Share this article, leave a comment, and let's keep the conversation going!
- The Most Hated Person In The World A Deeper Dive Into The Controversy
- The Perfect Temperature For Yeast A Deep Dive Into The Science Behind Breadmaking
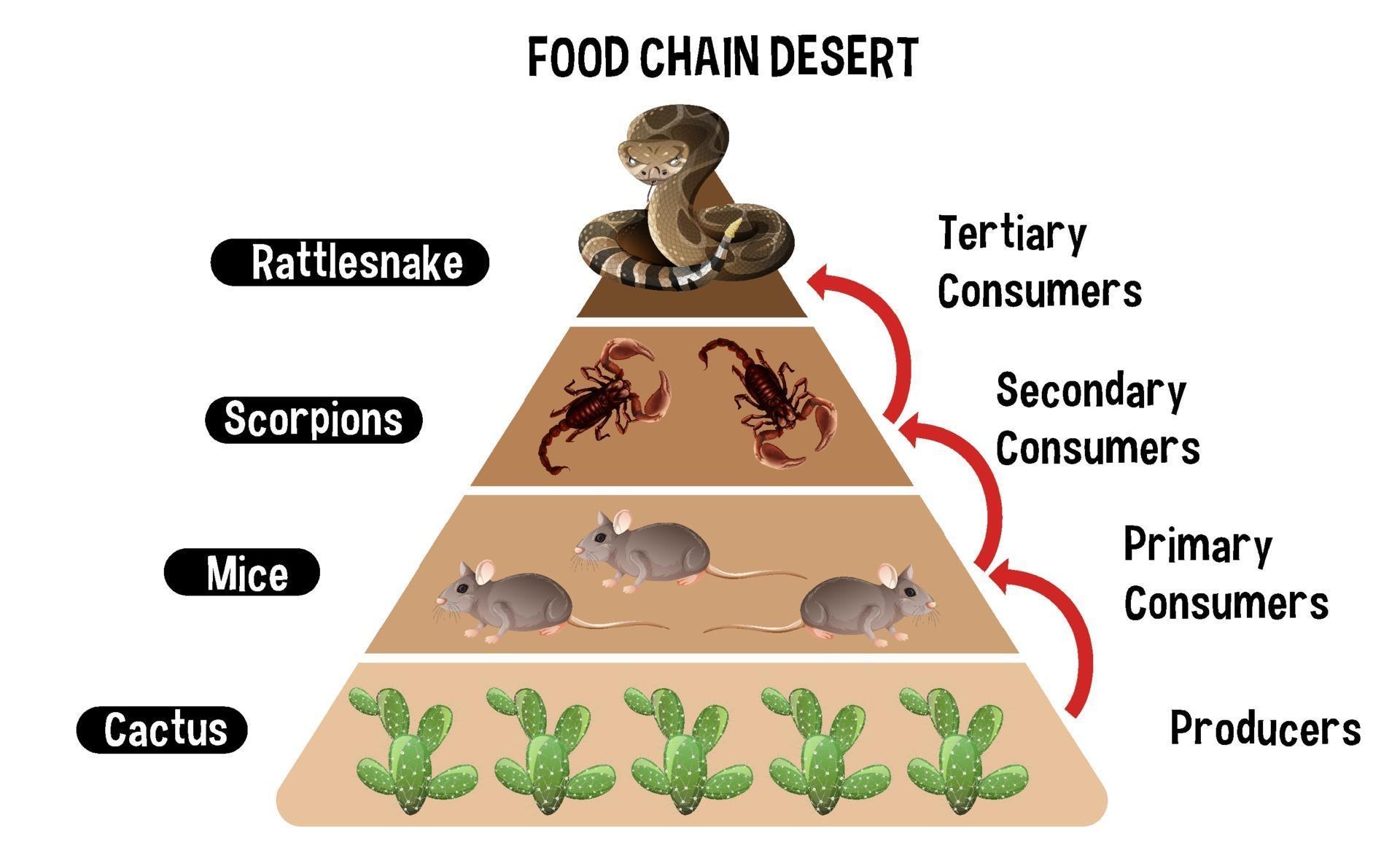
Diagram showing Desert food chain for education 2379595 Vector Art at
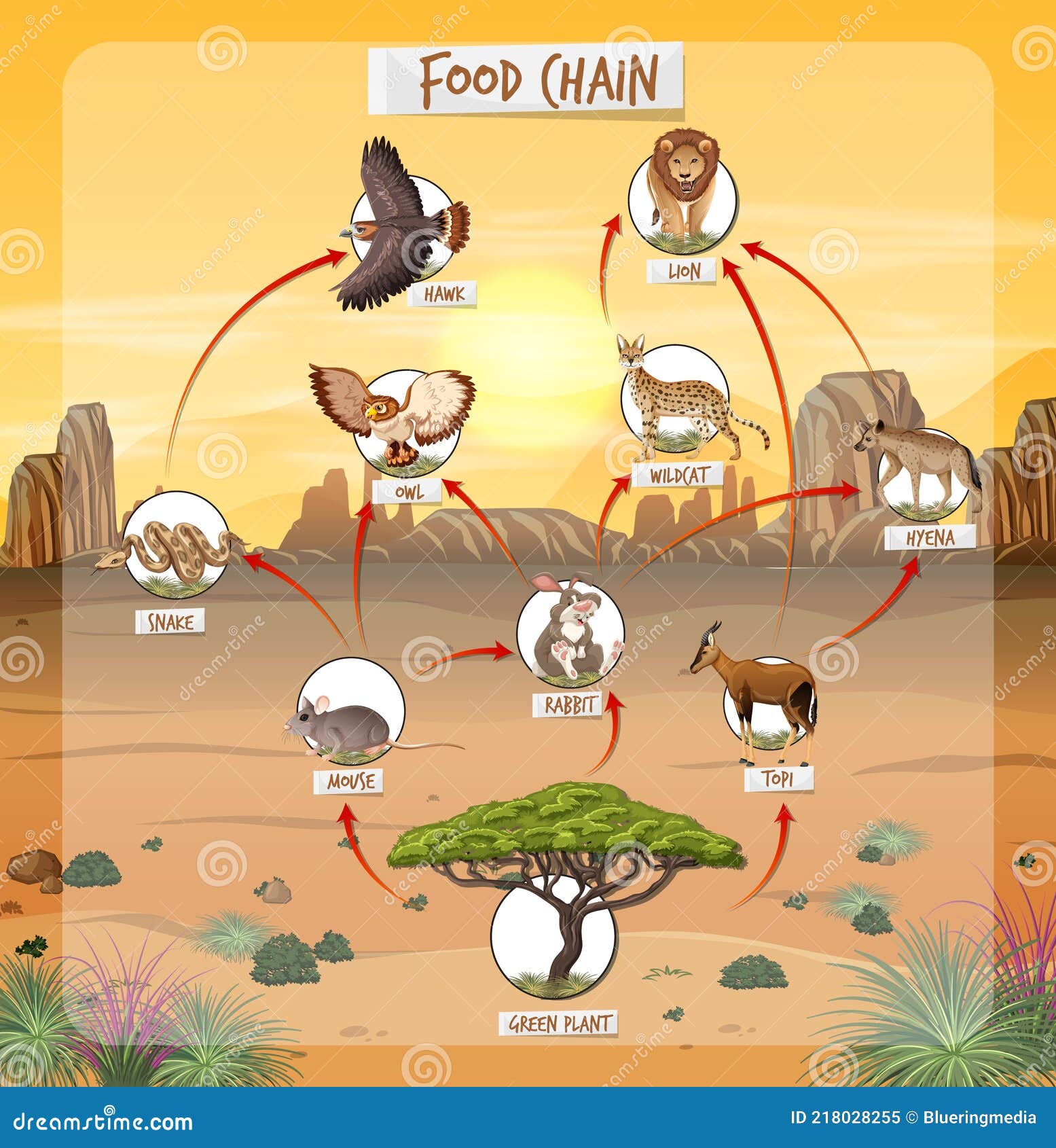
Sahara Desert Food Chain
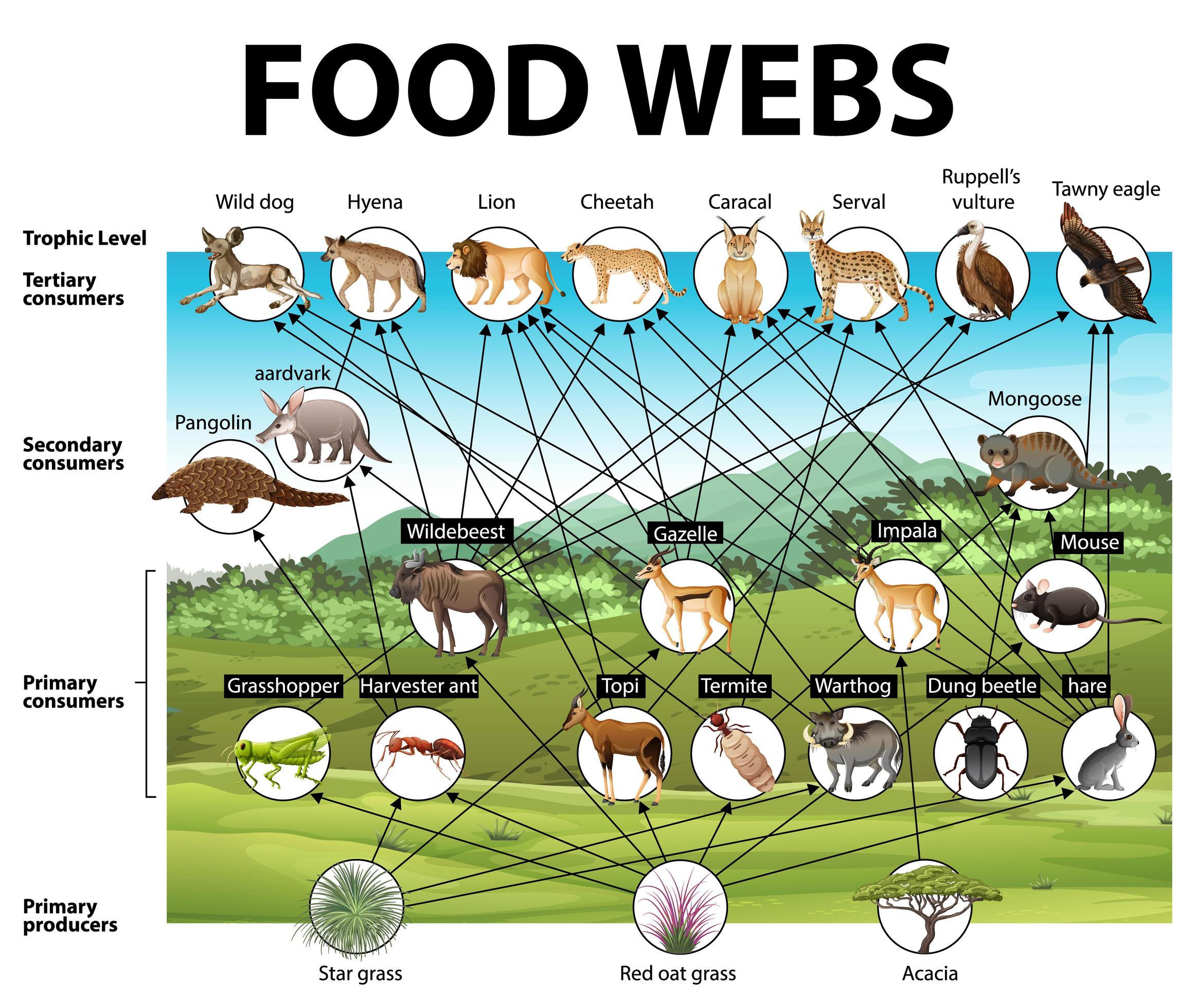
Education poster of biology for food webs diagram 1778184 Vector Art at