Alaska's Closest Point To Russia: A Fascinating Exploration
When you think about Alaska, one of the first things that might pop into your mind is its proximity to Russia. It's not just a random factoid; this geographical connection has deep historical and cultural significance. The closest point between Alaska and Russia is only about 55 miles apart, making it one of the most intriguing geographical features on the planet. So, buckle up as we dive deep into this fascinating topic and uncover some hidden gems about this unique relationship between two massive nations.
Alaska and Russia share a history that goes way back. The Russian-American Company established settlements in Alaska back in the late 18th century, and the region was even part of the Russian Empire for a while. This historical connection adds a layer of intrigue to the geographical closeness. Imagine sitting in a cozy cabin in Alaska and knowing that you're just a stone's throw away from another continent. It's wild, right?
Now, let's not forget why this matters. Understanding the closest point between Alaska and Russia isn't just about geography; it's about geopolitics, culture, and even tourism. People are genuinely curious about how close these two places are, and for good reason. It's not every day you get to explore the edge of one continent and peer into another. So, whether you're a history buff, a geography enthusiast, or just someone who loves a good story, this article is for you.
- Com Ed Outages The Power Struggles You Need To Understand Right Now
- Bad Traits Of Aquarius The Hidden Side Of The Water Bearer You Need To Know
Table of Contents
- Geographical Overview: Alaska's Closest Point to Russia
- Biogeographical Significance
- Historical Context: A Shared Past
- The Bering Strait: A Natural Bridge
- Islands in Focus: Diomede and Big Diomede
- The Travel Experience: Getting Up Close
- Cultural Impact: Bridging Two Worlds
- Climate and Weather: What to Expect
- Environmental Concerns: A Fragile Ecosystem
- Future Prospects: What Lies Ahead
Geographical Overview: Alaska's Closest Point to Russia
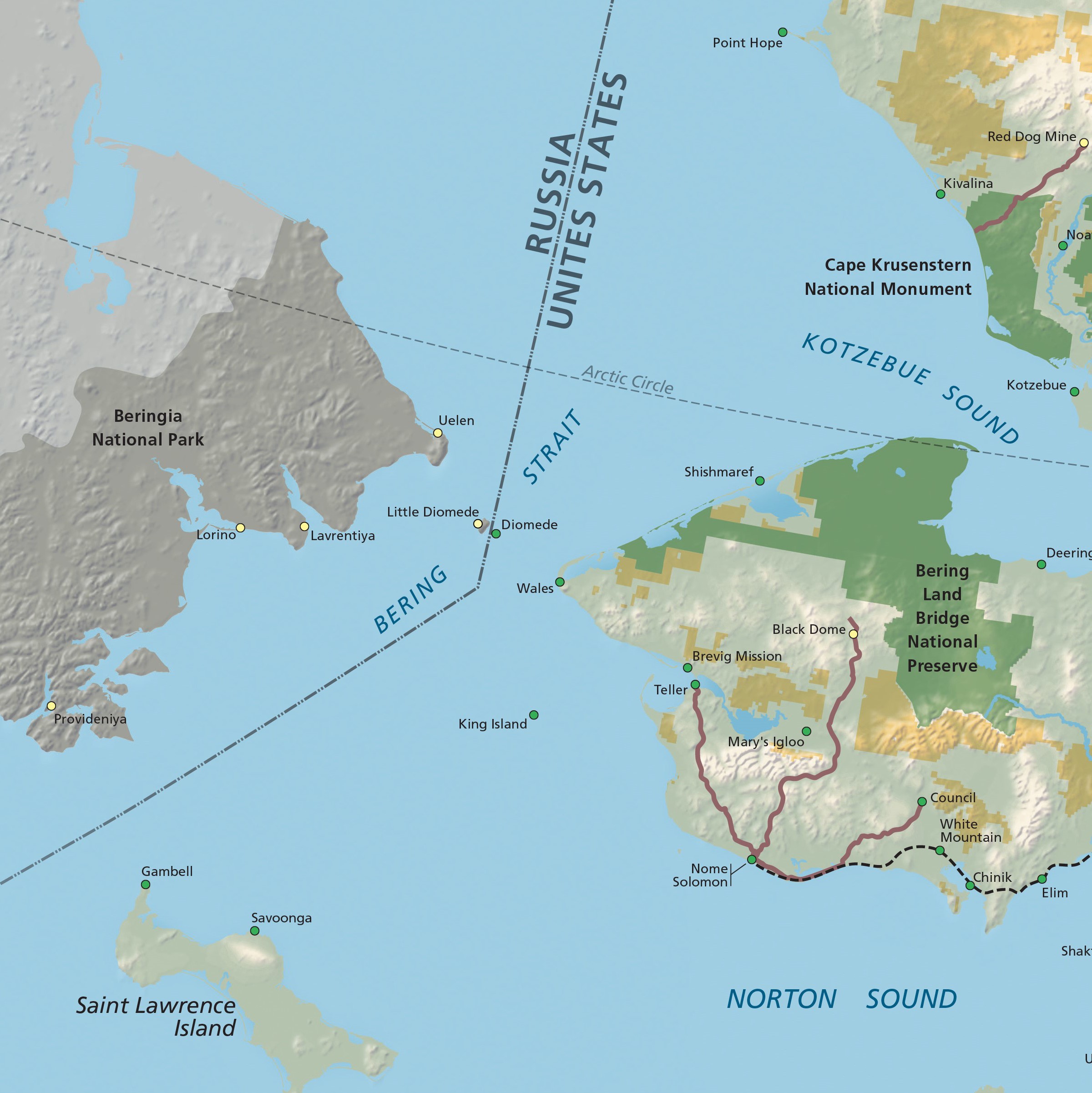
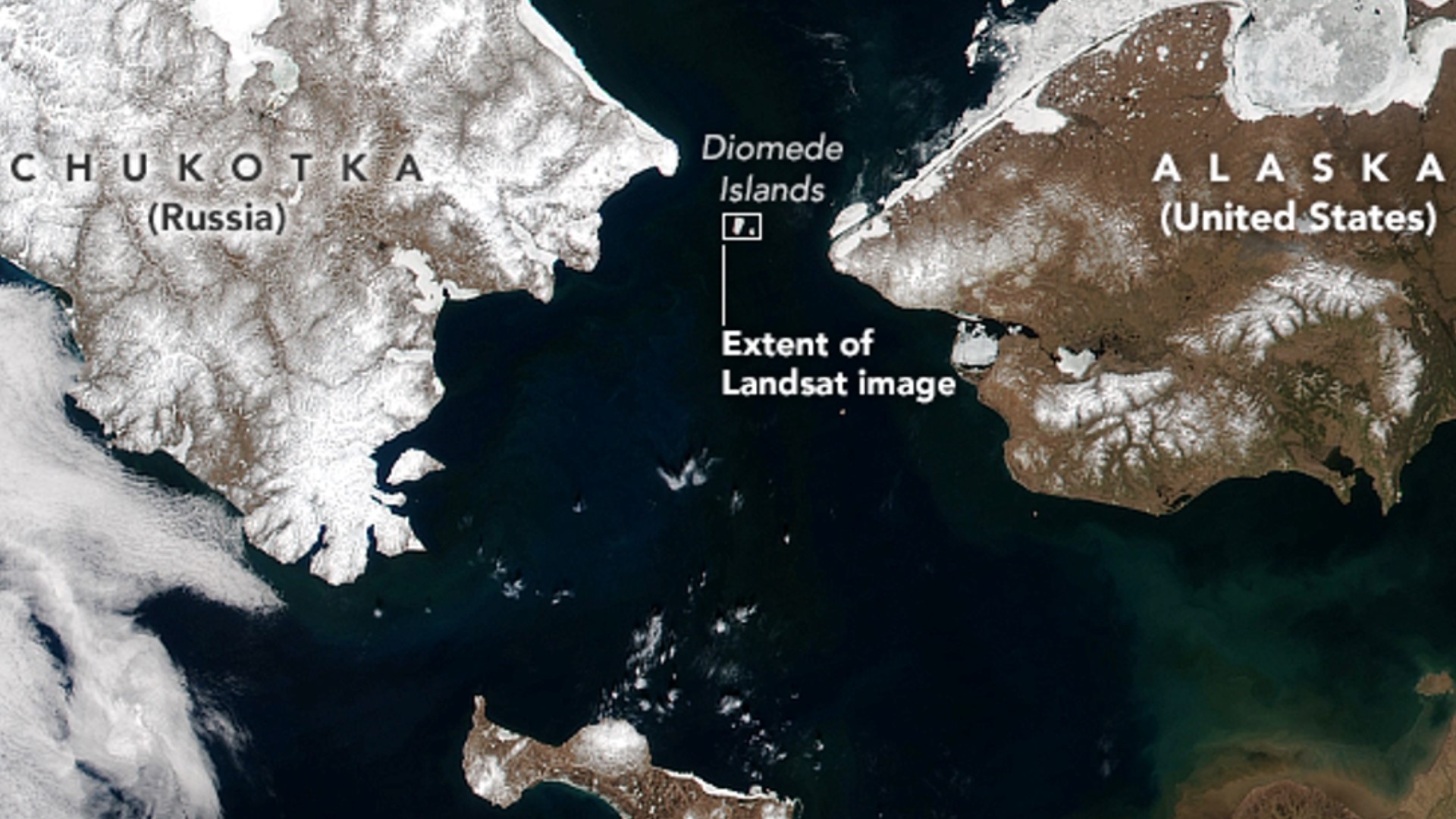
Alright, let's get down to the nitty-gritty. The closest point between Alaska and Russia is the Bering Strait, and within that strait lies the Diomede Islands. These islands are like the ultimate geographical bookends, with Little Diomede on the U.S. side and Big Diomede on the Russian side. The distance between these two islands? A mere 2.4 miles. Yup, you read that right—just 2.4 miles separate two continents.
The Bering Strait itself is about 55 miles wide, and it's the narrowest point between the two continents. This strait has been a crucial passageway for both animals and humans over thousands of years. Back in the day, during the Ice Age, the sea level was much lower, and a land bridge known as Beringia connected the two continents. This land bridge allowed early humans and animals to migrate from Asia to North America.
Why the Bering Strait Matters
The Bering Strait isn't just a geographical feature; it's a symbol of connection. It represents the blending of cultures, the movement of species, and the shared history of two massive regions. In today's world, where global connections are more important than ever, the Bering Strait serves as a reminder of how interconnected our planet truly is.
- What Does It Mean To Be Slu Footed Unveiling The Secrets Behind This Quirky Term
- Unveiling The Power Of Namari A Comprehensive Guide
Biogeographical Significance
When you think about the Bering Strait and the Diomede Islands, you're not just thinking about geography. You're diving into a world of biodiversity and ecological importance. This region is home to some of the most incredible wildlife on the planet. From walruses to polar bears, the area is teeming with life that thrives in one of the harshest environments on Earth.
Here are a few key points about the biogeographical significance of the region:
- The Bering Strait acts as a migration route for marine mammals, including whales, seals, and walruses.
- The area is a critical breeding ground for seabirds, with millions of birds nesting on the cliffs of the Diomede Islands.
- The cold waters of the strait support a diverse array of fish species, making it an important fishing ground.
Historical Context: A Shared Past
Alaska and Russia share a rich history that dates back centuries. The Russian Empire claimed Alaska in the late 18th century, and Russian settlers established trading posts and settlements throughout the region. The Russian-American Company played a significant role in the development of Alaska, and its influence can still be seen today in the architecture and culture of the region.
In 1867, the United States purchased Alaska from Russia for $7.2 million, a deal that became known as "Seward's Folly." At the time, many people thought the purchase was a waste of money, but it turned out to be one of the best real estate deals in history. Today, Alaska is a vibrant state with a unique blend of cultures, thanks in large part to its Russian heritage.
The Russian Influence
Even though Alaska is now part of the United States, the Russian influence is still evident. You can see it in the Orthodox churches scattered throughout the state, in the traditional crafts and art forms, and in the names of towns and landmarks. The connection between Alaska and Russia is a living, breathing part of the region's identity.
The Bering Strait: A Natural Bridge
The Bering Strait is more than just a body of water; it's a natural bridge that connects two continents. This strait has played a crucial role in the migration of species and the movement of people throughout history. During the Ice Age, when sea levels were much lower, a land bridge known as Beringia allowed early humans and animals to cross from Asia to North America.
Today, the Bering Strait is still a vital passageway for marine life and a symbol of the interconnectedness of our planet. The strait is also a focal point for geopolitical discussions, as it represents the boundary between two powerful nations.
Geopolitical Importance
The Bering Strait is not just a geographical feature; it's a geopolitical hotspot. The proximity of Alaska and Russia has led to numerous discussions about trade, security, and environmental protection. Both nations recognize the importance of this region and are working together to ensure its sustainability for future generations.
Islands in Focus: Diomede and Big Diomede
Let's zoom in on the Diomede Islands, the two tiny specks of land that sit right in the middle of the Bering Strait. Little Diomede is part of the United States, while Big Diomede belongs to Russia. The islands are separated by just 2.4 miles, making them the closest points between the two continents.
Here's a quick breakdown of the Diomede Islands:
- Little Diomede: Home to a small Native American community, the island is known for its stunning views and harsh weather conditions.
- Big Diomede: This island is uninhabited and serves as a military outpost for Russia. It's a reminder of the geopolitical tensions that exist in the region.
Life on the Diomede Islands
Living on the Diomede Islands is no walk in the park. The weather is extreme, and the isolation can be challenging. However, the people who call Little Diomede home have a deep connection to the land and a rich cultural heritage that dates back thousands of years.
The Travel Experience: Getting Up Close
If you're thinking about visiting the closest point between Alaska and Russia, you're in for an adventure. The region offers a unique travel experience that combines history, culture, and nature. Whether you're kayaking through the Bering Strait or visiting the Diomede Islands, you'll be treated to some of the most breathtaking scenery on the planet.
Here are a few tips for visiting the region:
- Plan ahead: The weather in the Bering Strait can be unpredictable, so make sure you check the forecast before you go.
- Respect the locals: The Native American communities in the region have a rich cultural heritage, so be sure to show respect and appreciation for their traditions.
- Bring your camera: The scenery is absolutely stunning, and you'll want to capture every moment.
Cultural Impact: Bridging Two Worlds
The connection between Alaska and Russia has had a profound impact on both cultures. The exchange of ideas, traditions, and technologies has enriched both regions and created a unique blend of influences. From the Orthodox churches in Alaska to the Russian language still spoken by some Native Alaskans, the cultural impact is undeniable.
This cultural bridge is a testament to the power of connection and the importance of understanding other cultures. In a world that often feels divided, the relationship between Alaska and Russia serves as a reminder of what we can achieve when we work together.
Climate and Weather: What to Expect
The climate in the Bering Strait region is harsh, to say the least. The winters are long and cold, with temperatures often dropping below zero. The summers are short and cool, with frequent fog and rain. However, this extreme climate is part of what makes the region so unique and beautiful.
Here are a few things to keep in mind about the climate:
- Winter temperatures can drop to -40°F or lower.
- Summer temperatures rarely exceed 60°F.
- Storms can be intense, so always be prepared for changing weather conditions.
Environmental Concerns: A Fragile Ecosystem
The Bering Strait region is home to a fragile ecosystem that is under threat from climate change and human activity. The melting of sea ice, overfishing, and pollution are all having a significant impact on the area. Both the United States and Russia are working together to address these issues and ensure the sustainability of the region.
Here are a few key environmental concerns:
- Melting sea ice: As the ice melts, it affects the habitat of marine mammals and birds.
- Overfishing: The demand for seafood is putting pressure on fish populations in the region.
- Pollution: Oil spills and other forms of pollution are threatening the delicate balance of the ecosystem.
Future Prospects: What Lies Ahead
Looking to the future, the relationship between Alaska and Russia will continue to evolve. Both nations recognize the importance of the Bering Strait region and are working together to address the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. From climate change to economic development, the possibilities are endless.
As we move forward, it's important to remember the lessons of the past and the connections that have been forged between these two regions. By working together, we can ensure a brighter future for both Alaska and Russia.
Final Thoughts
The closest point between Alaska and Russia is more than just a geographical feature; it's a symbol of connection, history, and culture. The Bering Strait and the Diomede Islands remind us of the power of nature and the importance of understanding our shared past. Whether you're a traveler, a historian, or just someone who loves a good story, this region has something to offer everyone.
So, what are you waiting for? Dive into the world of Alaska and Russia and discover the incredible stories that lie just beyond the horizon. And don't forget to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below!
- Fast Food Champaign Il Your Ultimate Guide To Tasty Eats
- Did Joyce Dewitt Die The Truth Behind The Rumors
How Close is Alaska to Russia? Alaska Public Lands (U.S. National
How far is Russia from the United States

Alaska Bridge Between U.S. and Russia