Food Web For The Everglades: A Comprehensive Guide To Nature's Delicate Balance
Picture this, y’all: the Everglades, a vast, wet, wild stretch of land where nature thrives in all its glory. The food web for the Everglades is like a big ol’ puzzle, where every piece plays a crucial role in keeping the ecosystem alive and kicking. From the tiniest insects buzzing around to the massive alligators lurking in the water, everything’s interconnected in this swampy paradise. And guess what? This intricate food web is what keeps the Everglades alive and thriving, even in the face of challenges.
Now, you might be wondering, why does the food web for the Everglades matter so much? Well, my friend, it’s not just about animals munching on each other—it’s about balance. The Everglades is one of the most unique ecosystems on the planet, and understanding how its food web works can help us protect it for future generations. Think of it as a recipe for nature’s survival, where every ingredient counts.
But hold up, before we dive deeper into the nitty-gritty of the food web for the Everglades, let’s take a moment to appreciate how fascinating this whole thing is. The Everglades isn’t just a bunch of swamps and marshes—it’s a living, breathing ecosystem that’s been around for thousands of years. So, buckle up, because we’re about to explore the ins and outs of this incredible food web and why it matters so much.
- Best Korean Food In Vegas A Musttry Culinary Adventure
- James Hardens Son The Untold Story Of Fatherhood Beyond The Court
What is the Food Web for the Everglades?
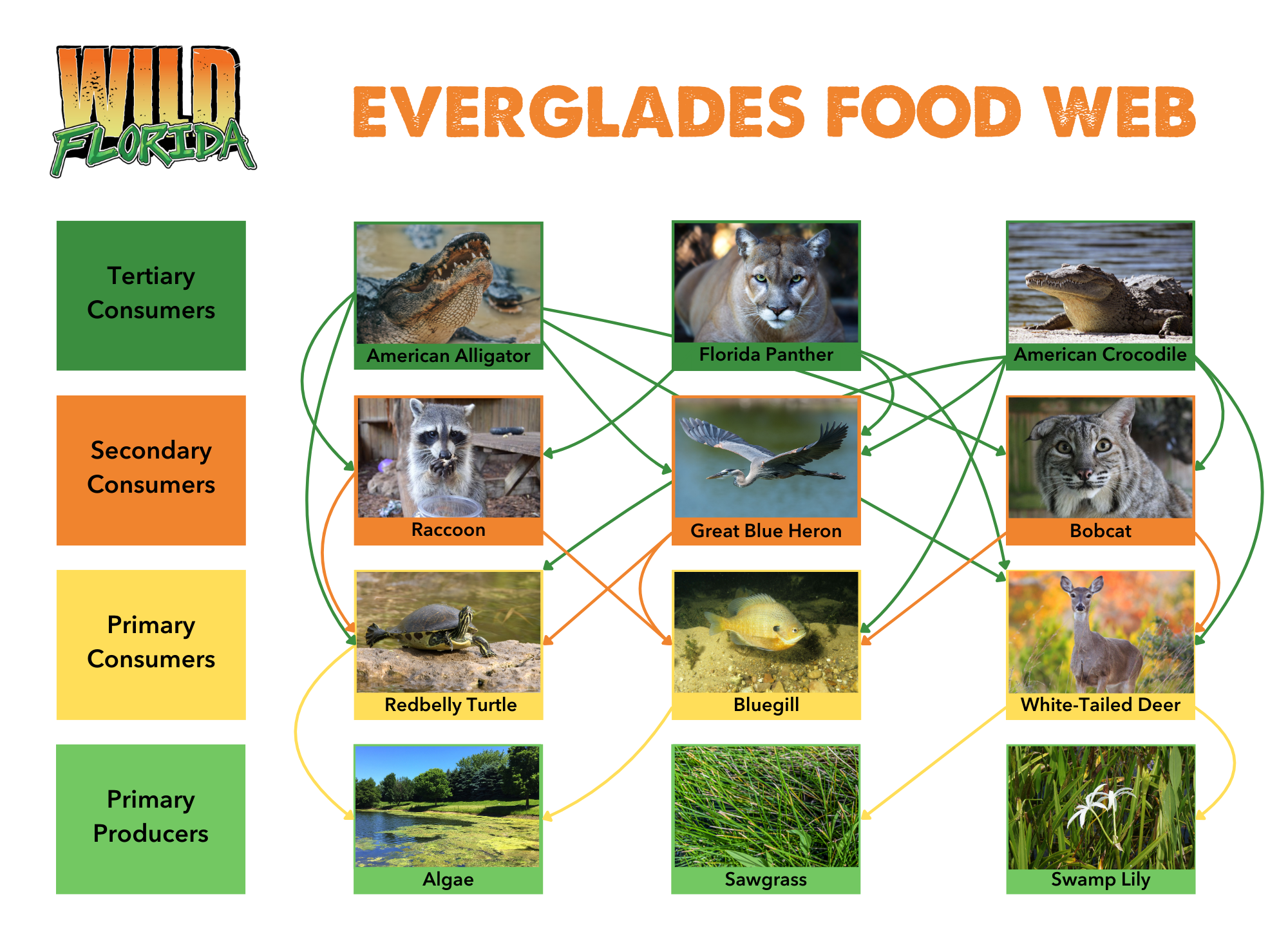
Alright, let’s break it down. The food web for the Everglades is basically a map of who eats whom in this wetland wonderland. It’s like a big ol’ dinner party where everyone has a role to play. At the bottom of the food chain, you’ve got the producers—plants like sawgrass and periphyton that soak up the sun and turn it into energy. These little guys are the foundation of the whole system, and without them, the entire food web would collapse.
Then you’ve got the consumers, which are divided into three main groups: primary, secondary, and tertiary. Primary consumers are herbivores like apple snails and marsh rabbits that munch on plants. Secondary consumers are carnivores that eat the herbivores, like fish and wading birds. Finally, you’ve got the tertiary consumers, the big bosses of the food web—think alligators and panthers. These apex predators keep the population of smaller animals in check, ensuring that no one group gets too out of control.
And let’s not forget the decomposers, the unsung heroes of the food web. These little critters—like fungi and bacteria—break down dead plants and animals, recycling nutrients back into the soil. It’s a full-circle system, where nothing goes to waste, and everything contributes to the greater good of the ecosystem.
- Mlp Transcript Envy A Deep Dive Into The World Of Friendship And Jealousy
- Batiste Wife The Untold Story Of Love Fame And Life In The Spotlight
Why is the Food Web for the Everglades Important?
Here’s the thing: the food web for the Everglades isn’t just some random collection of animals eating each other. It’s a finely tuned machine that keeps the ecosystem healthy and balanced. When one part of the food web gets out of whack, it can have a ripple effect that impacts the entire system. For example, if the population of apple snails drops because of pollution, the birds that rely on them for food could also start to decline. And if the birds disappear, the predators that eat them might struggle to survive.
See how it all connects? That’s why understanding the food web for the Everglades is so important. By studying how different species interact with each other, scientists can identify potential threats to the ecosystem and come up with strategies to protect it. Whether it’s invasive species, climate change, or human activity, every little thing can have a big impact on the delicate balance of the Everglades’ food web.
Producers: The Foundation of the Everglades Food Web
Let’s talk about the producers, the backbone of the Everglades food web. These are the plants that convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis, providing the fuel that powers the entire ecosystem. The most iconic producer in the Everglades is sawgrass, which covers vast areas of the wetlands. Sawgrass isn’t actually grass—it’s a type of sedge—but it’s one of the most important plants in the Everglades, providing habitat and food for countless species.
Another key player in the producer category is periphyton, a type of algae that grows on the surface of the water. Periphyton might not be the prettiest thing in the world, but it’s super important for the food web. It provides food for tiny aquatic organisms like insects and snails, which in turn are eaten by larger animals. Without periphyton, the entire food web would be in big trouble.
And let’s not forget about the trees, like cypress and mangroves, which provide shade, shelter, and nesting sites for birds and other animals. These trees are like nature’s skyscrapers, creating a vertical habitat that adds complexity to the food web. So, the next time you’re walking through the Everglades and see a tree, give it a little nod of appreciation—it’s doing its part to keep the ecosystem running smoothly.
Primary Consumers: The Herbivores of the Everglades
Now let’s move up the food chain to the primary consumers, the herbivores that munch on plants. These animals are the bridge between the producers and the carnivores, converting plant energy into animal energy. One of the most important primary consumers in the Everglades is the apple snail, a little critter that’s a favorite food of many wading birds.
Apple snails are like nature’s gardeners, helping to control the growth of aquatic plants and keeping the ecosystem in balance. But here’s the thing: apple snails are also a favorite snack for invasive species like the island apple snail, which can outcompete the native species and disrupt the food web. This is just one example of how invasive species can throw a wrench into the delicate balance of the Everglades’ food web.
Another key primary consumer is the marsh rabbit, a small mammal that feeds on grasses and other vegetation. Marsh rabbits are an important food source for predators like bobcats and birds of prey, and their population can have a big impact on the rest of the food web. So, the next time you see a marsh rabbit hopping around, remember that it’s playing an important role in the ecosystem.
Secondary Consumers: The Carnivores of the Everglades
Alright, let’s talk about the secondary consumers, the carnivores that eat the herbivores. These animals are like the middle managers of the food web, keeping the population of primary consumers in check. One of the most iconic secondary consumers in the Everglades is the American alligator, a reptile that’s been around for millions of years.
Alligators are like nature’s garbage disposals, eating just about anything that crosses their path. They help control the population of fish, turtles, and other animals, ensuring that no one species becomes too dominant. But here’s the thing: alligators are also a keystone species, meaning they play a crucial role in maintaining the structure of the ecosystem. Without alligators, the Everglades would be a very different place.
Another important secondary consumer is the great blue heron, a wading bird that feeds on fish, frogs, and other aquatic animals. Great blue herons are like nature’s anglers, using their long necks and sharp beaks to catch their prey. They’re also an indicator species, meaning their population can tell us a lot about the health of the ecosystem. If the great blue heron population starts to decline, it could be a sign that something’s wrong with the food web.
Tertiary Consumers: The Apex Predators of the Everglades
Now we’re getting to the top of the food chain, the tertiary consumers, or apex predators. These animals are the kings and queens of the Everglades, ruling the ecosystem with an iron claw. The most famous tertiary consumer in the Everglades is the Florida panther, a majestic big cat that’s one of the rarest animals in the world.
Florida panthers are like nature’s assassins, stalking their prey with stealth and precision. They help control the population of deer, hogs, and other animals, ensuring that the ecosystem stays in balance. But here’s the thing: Florida panthers are also an endangered species, with only about 120 individuals left in the wild. Protecting these magnificent creatures is crucial for maintaining the health of the Everglades’ food web.
Another important tertiary consumer is the American crocodile, a distant cousin of the alligator that’s found in the southern part of the Everglades. Crocodiles are like nature’s bodyguards, keeping the waters safe from invasive species and other threats. They’re also an indicator species, meaning their population can tell us a lot about the health of the ecosystem. So, the next time you see a crocodile basking in the sun, remember that it’s playing an important role in the food web.
Decomposers: The Unsung Heroes of the Everglades
Alright, let’s talk about the decomposers, the unsung heroes of the Everglades food web. These little critters might not get a lot of attention, but they’re super important for the ecosystem. Decomposers like fungi and bacteria break down dead plants and animals, recycling nutrients back into the soil and keeping the cycle of life going.
One of the most important decomposers in the Everglades is the mushroom, a fungus that grows on decaying wood and other organic matter. Mushrooms might not be the most glamorous organisms in the world, but they’re like nature’s recyclers, turning waste into valuable nutrients for the ecosystem. Without mushrooms, the Everglades would be a very different place.
Another key decomposer is the bacteria, tiny microorganisms that live in the water and soil. Bacteria might be invisible to the naked eye, but they’re super important for breaking down organic matter and releasing nutrients into the environment. So, the next time you take a sip of water from the Everglades, remember that it’s full of tiny bacteria that are working hard to keep the ecosystem healthy.
Threats to the Food Web for the Everglades
Now, let’s talk about the threats to the food web for the Everglades. Unfortunately, this incredible ecosystem is facing a lot of challenges, from climate change to human activity. One of the biggest threats is invasive species, like the Burmese python, which has been wreaking havoc on the food web by eating native animals and outcompeting them for resources.
Another major threat is pollution, which can harm plants and animals and disrupt the delicate balance of the food web. Nutrient pollution from agricultural runoff, for example, can cause algae blooms that block sunlight and kill aquatic plants, affecting the entire food chain. And let’s not forget about climate change, which is causing sea levels to rise and altering the habitat of many species in the Everglades.
But here’s the good news: there are things we can do to protect the food web for the Everglades. By supporting conservation efforts, reducing pollution, and controlling invasive species, we can help ensure that this incredible ecosystem continues to thrive for generations to come.
Conservation Efforts for the Everglades Food Web
Alright, let’s talk about conservation efforts for the Everglades food web. There are a lot of people and organizations working hard to protect this incredible ecosystem, and their efforts are making a real difference. One of the most important conservation initiatives is the Comprehensive Everglades Restoration Plan (CERP), a massive project aimed at restoring the natural flow of water through the Everglades and improving the health of the ecosystem.
CERP involves a wide range of activities, from removing levees and canals to restoring wetlands and improving water quality. By restoring the natural hydrology of the Everglades, scientists hope to improve the habitat for native species and reduce the impact of invasive species. It’s a big undertaking, but it’s already showing signs of success, with populations of some species starting to recover.
Another important conservation effort is the work being done to protect endangered species like the Florida panther and the wood stork. Through habitat restoration, captive breeding programs, and other strategies, scientists are working to bring these species back from the brink of extinction. And let’s not forget about the work being done to control invasive species like the Burmese python, which is crucial for maintaining the balance of the food web.
How You Can Help Protect the Everglades Food Web
So, what can you do to help protect the food web for the Everglades? Well, there are a lot of things you can do, even if you don’t live in Florida. For starters, you can support conservation organizations that are working to protect the Everglades, either through donations or volunteer work. You can also reduce your own environmental impact by conserving water, reducing pollution, and supporting sustainable practices.
Another thing you can do is educate yourself and others about the importance of the Everglades and its food web. By spreading awareness about this incredible ecosystem, you can help inspire others to take action and make a difference. And if you ever get the chance to visit the Everglades, take it! Seeing this amazing place firsthand can be a powerful motivator for protecting it.
Conclusion: The Importance of the Food Web for the Everglades
- The Most Hated Person In The World A Deeper Dive Into The Controversy
- Incredibles Villain The Ultimate Guide To Their Backstories And Powers
The Everglades Food Web A Unique Ecosystem

Choose one of the food chains shown within the food web in Figure 34
Everglades Food Web Ecosystems How Everything Works Together My XXX