Desert Food Web: Unlocking The Secrets Of Life In Arid Ecosystems
Hey there, nature enthusiasts! If you're diving into the world of desert ecosystems, you're about to uncover something truly fascinating. The desert food web is a complex yet delicate system that supports life in some of the harshest environments on our planet. Think about it—how do organisms survive in places where water is scarce and temperatures can swing wildly from scorching hot to freezing cold? Stick around, because we're about to break it all down for you.
Now, let's get one thing straight: the desert food web isn't just about cacti and sand. It's a vibrant network of interactions between plants, animals, and microorganisms that keep the ecosystem balanced. Whether you're a student, an environmentalist, or just someone who's curious about the wonders of nature, this article will give you the lowdown on how life thrives in the desert.
So, buckle up and get ready to dive deep into the world of desert food webs. We'll explore the key players, their roles, and how they all fit together to create a thriving ecosystem. By the end of this, you'll have a whole new appreciation for the resilience of life in the desert.
- Tiny Harris Younger The Rising Star You Need To Know
- Matt Gaetz Hacked The Inside Story You Need To Know
Here's a quick roadmap to guide you through this article:
- Introduction to Desert Food Web
- Biotic Components of the Desert
- Abiotic Components of the Desert
- Primary Producers in the Desert
- Primary Consumers: The Herbivores
- Secondary Consumers: The Carnivores
- Decomposers: Nature's Clean-Up Crew
- Understanding the Dynamics of the Food Web
- Human Impact on Desert Ecosystems
- Conservation Efforts for Desert Food Webs
Introduction to Desert Food Web
Alright, let's kick things off with a little background on what exactly a desert food web is. Simply put, it's the interconnected system of who eats whom in the desert. But it's not as simple as it sounds. Every creature, from the tiniest insect to the largest predator, plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of the ecosystem.
The desert food web is a bit like a game of survival. Organisms have to adapt to extreme conditions, and they do so in some pretty amazing ways. Some plants store water in their tissues, while others have deep roots to access underground water sources. Animals, on the other hand, have developed strategies like nocturnal behavior to avoid the heat and conserve energy.
- Ariana Grande Concert Dates The Ultimate Guide For Fans
- Axl Rose 2024 The Legend Continues Heres Everything You Need To Know
So, why is the desert food web important? Well, it's not just about the desert itself. The health of desert ecosystems can have a ripple effect on the planet as a whole. They influence global climate patterns, provide habitat for unique species, and even offer lessons in sustainability that we can apply to our own lives.
Biotic Components of the Desert
Flora and Fauna of the Desert
The biotic components of the desert food web include all the living organisms that call the desert home. This ranges from plants like cacti and succulents to animals like reptiles, insects, and mammals. Each of these organisms has its own niche in the ecosystem, contributing to the overall balance.
For example, cacti and other drought-resistant plants provide food and shelter for herbivores. These herbivores, in turn, become prey for carnivores higher up the food chain. It's a delicate balance, and any disruption can have serious consequences for the entire ecosystem.
Here are a few key players in the biotic components of the desert:
- Cacti and other drought-resistant plants
- Herbivorous insects and mammals
- Carnivorous reptiles and mammals
- Scavengers and decomposers
Abiotic Components of the Desert
The Role of Non-Living Factors
While the biotic components are the living organisms, the abiotic components are the non-living factors that influence the desert food web. These include things like temperature, sunlight, and water availability. In the desert, these factors can be extreme, shaping the way organisms adapt and interact.
For instance, the intense sunlight and lack of water mean that plants have to be highly efficient at photosynthesis and water conservation. Animals, too, have to adapt to the heat and dryness, often by being active during cooler parts of the day.
Here are some of the key abiotic factors in the desert:
- Temperature extremes
- Limited water availability
- Strong sunlight and UV radiation
- Wind and sand movement
Primary Producers in the Desert
Primary producers are the foundation of the desert food web. These are the plants and algae that use sunlight to produce energy through photosynthesis. In the desert, primary producers have to be tough. They need to survive with minimal water and withstand intense heat.
Some common primary producers in the desert include:
- Cacti
- Succulents
- Desert grasses
- Shrubs
These plants provide the energy that fuels the entire food web. They're like the power plants of the desert, converting sunlight into food for herbivores and, indirectly, for carnivores as well.
Primary Consumers: The Herbivores
Primary consumers are the next level up in the desert food web. These are the herbivores that feed directly on the primary producers. In the desert, you'll find a variety of herbivores, from tiny insects to larger mammals like kangaroo rats and jackrabbits.
Herbivores play a crucial role in the food web by converting plant material into biomass that can be consumed by carnivores. They also help to control plant populations, preventing any one species from becoming too dominant.
Here are some examples of primary consumers in the desert:
- Grasshoppers
- Caterpillars
- Kangaroo rats
- Jackrabbits
Secondary Consumers: The Carnivores
Secondary consumers are the carnivores that feed on the herbivores. In the desert, these include predators like snakes, lizards, and birds of prey. Carnivores help to regulate the populations of herbivores, ensuring that the ecosystem remains balanced.
Some of the most fascinating secondary consumers in the desert include:
- Rattlesnakes
- Desert tortoises
- Red-tailed hawks
- Coyotes
These predators are often highly adapted to the desert environment, with keen senses and stealthy hunting techniques that allow them to thrive in such a challenging landscape.
Decomposers: Nature's Clean-Up Crew
Decomposers are the unsung heroes of the desert food web. These are the organisms that break down dead plant and animal material, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem. Without decomposers, the desert would quickly become a wasteland of rotting matter.
Some common decomposers in the desert include:
- Fungi
- Bacteria
- Scavenger insects like beetles
These organisms play a vital role in maintaining the health of the ecosystem by ensuring that nutrients are continuously cycled through the food web.
Understanding the Dynamics of the Food Web
The dynamics of the desert food web are complex and constantly changing. Factors like climate, human activity, and natural disasters can all impact the balance of the ecosystem. For example, a prolonged drought can reduce the availability of water, affecting both plants and animals.
On the other hand, conservation efforts and sustainable land management can help to maintain the health of the desert food web. By protecting key species and habitats, we can ensure that this delicate system continues to thrive.
Here are some of the key dynamics at play in the desert food web:
- Energy flow from producers to consumers
- Nutrient cycling through decomposition
- Predator-prey relationships
- Competition for resources
Human Impact on Desert Ecosystems
Let's talk about the elephant in the room: humans. Our activities can have a significant impact on desert ecosystems, often disrupting the delicate balance of the food web. Things like urbanization, agriculture, and climate change can all lead to habitat loss, pollution, and changes in water availability.
However, it's not all doom and gloom. There are steps we can take to minimize our impact and protect these vital ecosystems. By practicing sustainable land use, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and supporting conservation efforts, we can help to preserve the desert food web for future generations.
Conservation Efforts for Desert Food Webs
Finally, let's talk about what's being done to protect the desert food web. Conservationists around the world are working hard to preserve these unique ecosystems, from establishing protected areas to restoring degraded habitats.
Some of the most effective conservation strategies include:
- Creating wildlife corridors to connect fragmented habitats
- Restoring native vegetation to support biodiversity
- Monitoring populations of key species to ensure their survival
- Engaging local communities in conservation efforts
By working together, we can ensure that the desert food web remains a vibrant and thriving part of our planet's natural heritage.
Conclusion
And there you have it—a deep dive into the world of desert food webs. From the primary producers to the top predators, every organism plays a vital role in maintaining the balance of this unique ecosystem. Understanding the dynamics of the desert food web not only helps us appreciate the resilience of life in the desert but also highlights the importance of protecting these fragile environments.
So, what can you do to help? Start by learning more about desert ecosystems and sharing your knowledge with others. Support conservation organizations working to protect these vital habitats. And most importantly, take steps in your own life to reduce your impact on the planet. Together, we can make a difference.
Thanks for joining me on this journey through the desert food web. If you enjoyed this article, don't forget to leave a comment, share it with your friends, and check out some of our other articles on nature and the environment. Until next time, keep exploring and stay curious!
- Exploring The Best Las Vegas Airport Terminal 3 Restaurants
- Liberte Chan How Old Discovering The Rising Starrsquos Age And Journey
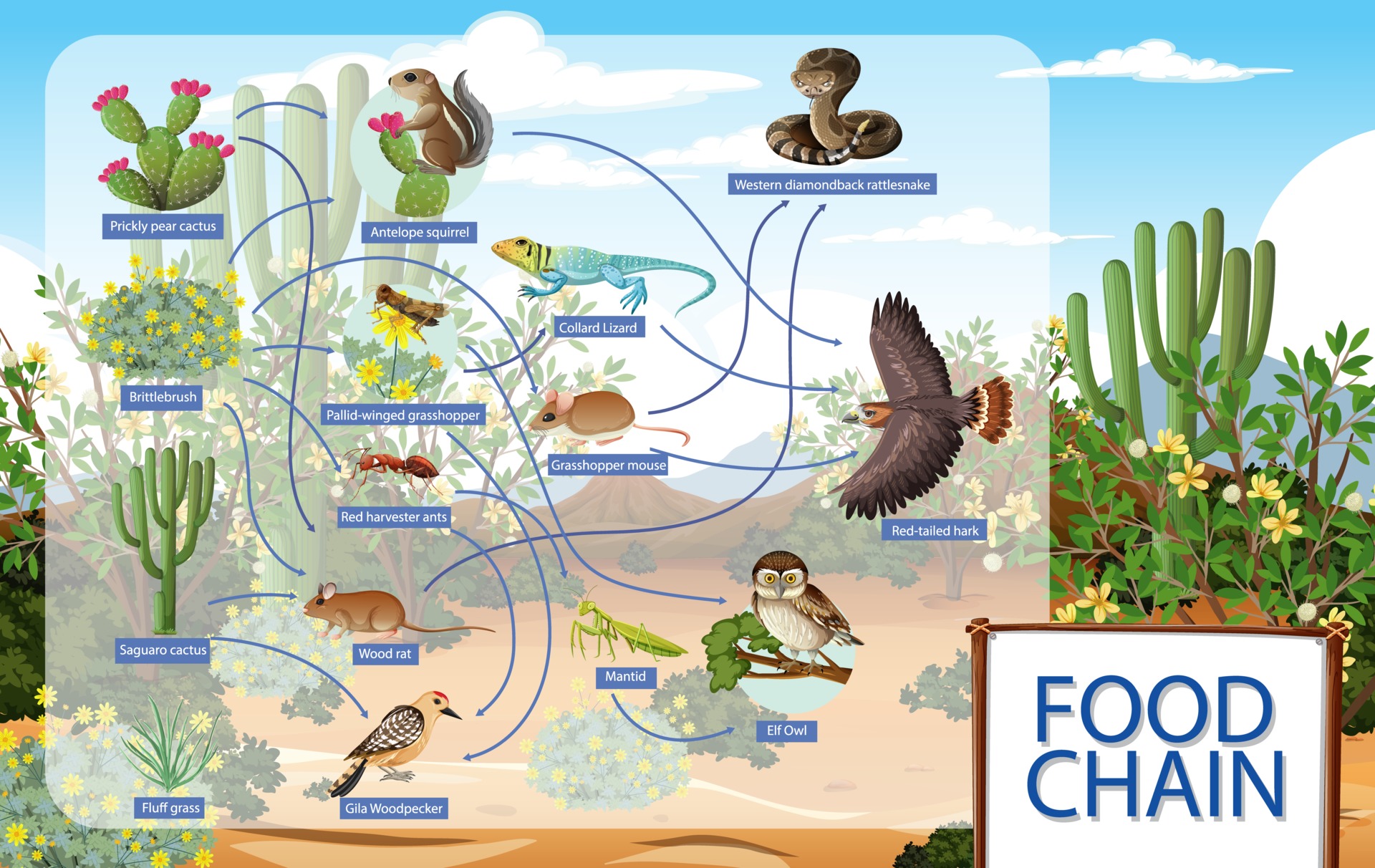
Diagram showing desert animals food chain 2952865 Vector Art at Vecteezy
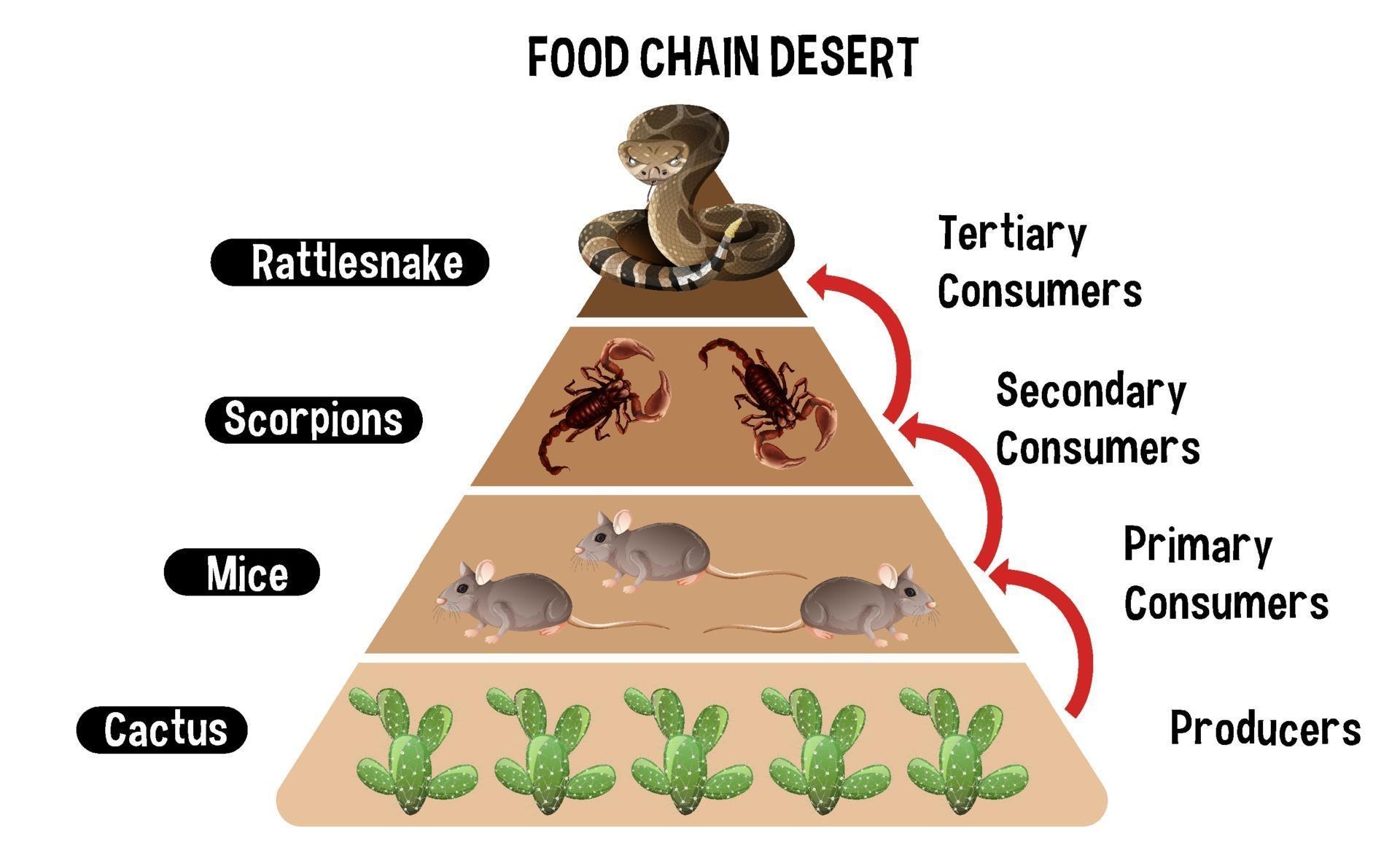
Diagram showing Desert food chain for education 2379595 Vector Art at

Sonoran Desert food web